Most accessory makers tend to build accessories for the more dominant platforms, which is why a lot of computer peripherals tend to be more focused towards Windows users. This can make it a bit tricky if you’re a Mac user, especially if you’re looking to buy an external hard drive where sometimes, some models might come preformatted for Windows use.
We’re sure that some of you have encountered situations where you plug in an external hard drive or USB flash drive to your Mac computer, only to find that it won’t read or you can make changes to it due to it being formatted only for Windows. However, if you’re looking to ensure full compatibility between Windows and Mac, check out the steps below.
How To Format An External Hard Drive For Mac
The process to format an external hard drive or USB flash drive for your Mac is pretty easy and straightforward.
- Plug in your external hard drive or USB flash drive to your Mac computer
- Launch the Disk Utility app which can be found in Applications > Other
- Select the drive from the left side of the window
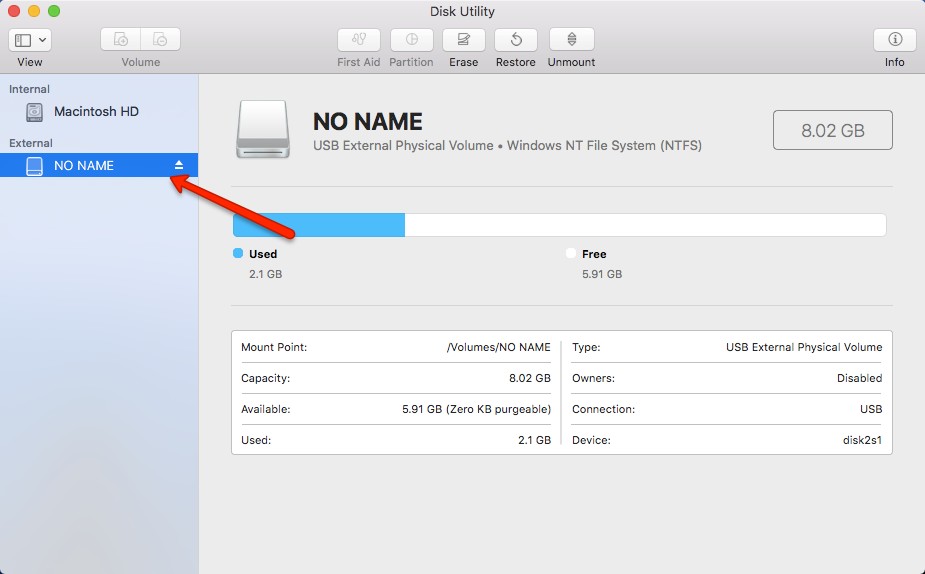
- Click the Erase tab at the top of the screen

- Under Format, select ExFAT

- Click Erase and depending on how much you have stored on it, it could take seconds or minutes to complete.
- Once completed, you should see the new file type of your hard drive (note that prior to formatting it said NTFS).

Which File Format Should I Use?
During the process of formatting your hard drive, under the Format section you would have noticed that there are quite a few different options for you to choose from, so the question is, what are the differences between the file formats and which should you choose?
ExFAT
This is the option that we told you that you should choose if you wish to ensure that your hard drive will be compatible (which means that it can read and write) on both Windows and Mac computer systems.
MS-DOS FAT
Also known as FAT32 on some systems, this is another option that you can choose if you want to format a hard drive that will be compatible across Windows and Mac. However, one of the main differences between FAT32 and ExFat is that the former will only support file sizes of up to 4GB. This means that if you’re looking to transfer a video file that’s over 4GB in size, you will not be able to. This is due to the fact that FAT32 is an older file system.
APFS (Apple File System)
This is a newer file system that Apple introduced with its High Sierra update. It will be the default format that will be used for internal drives and also newer external hard drives that are designed specifically for Mac use. The upside is that it is more efficient, more reliable, and users can also choose to have it encrypted to protect the contents of their computer.
The downside is that it will not be compatible with older versions of macOS and will also not be compatible with Windows or Linux machines. However, if you’re only using Mac computers then this could be an option to consider.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled)
This file format was also previously known as HFS+. It was the file system that Apple had used prior to introducing APFS. For older Mac computers that do not run High Sierra or newer, Mac OS Extended will be the default format of choice. Similar to APFS, there are options to have it encrypted and password protected, and also users can choose to format it so that it can be case-sensitive for files that might require them.
Also, just like APFS, Mac OS Extended is not readable on Windows machines, so if you’re looking for cross-platform compatibility, ExFAT is still the best choice for now.
Filed in . Read more about Mac (Apple), Microsoft and Windows.


